A Cdma Receiver Gets the Following Chips
Data Communications and Networks Spring 2020 Assignment 3 Due April 24 1. In digital communications a chip is a pulse of a direct-sequence spread spectrum code such as a pseudo-random noise code sequence used in direct-sequence code-division multiple access channel access techniques.

Solved 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips Chegg Com
Assuming the chip sequences defined as follows.
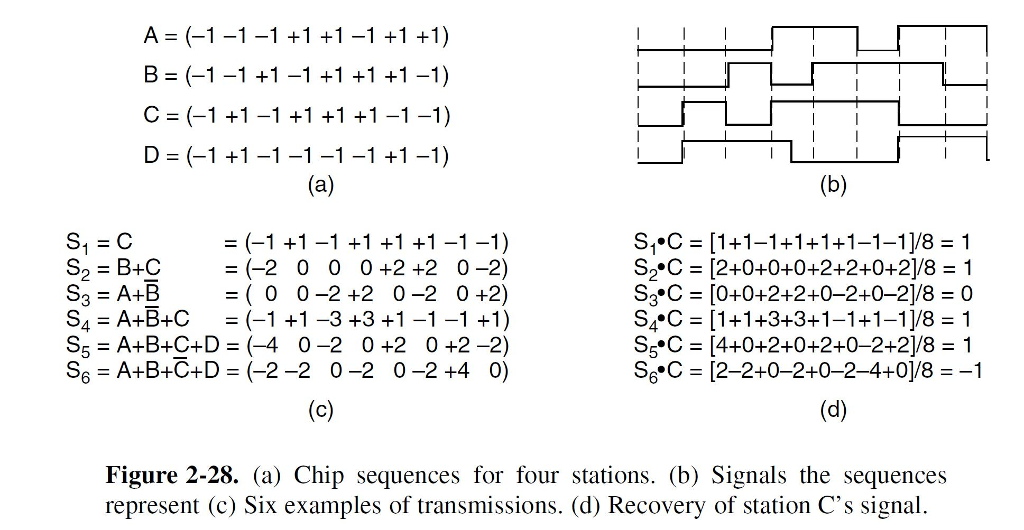
. Assuming the chip sequences defined in Figure 1 which stations transmitted and which bits. 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 Chip. -1-1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1 C.
Assuming the chip sequences defined in Figure 1 which stations transmitted and which bits ie. -1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1 -1 A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. Bit 0 or bit 1 did each station send.
And it provides zero cross-correlation among all the other users. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. Assume the chip sequences defined in Figure.
15 points A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. Assume the chip sequences defined in Figure. A Chip sequences for four stations.
2-45 b which stations transmited and which bits did each one send. -1 1 -3 1 -1 -3 1 1. Where n is a power of 2 and indicates the different dimensions of the matrix W.
In a binary direct-sequence system each chip is typically a rectangular pulse of 1 or 1 amplitude which is multiplied by a data sequence and by a carrier. We know that c is 3x10⁸ ms. W A -1-1 -1 1 1 -1 1 1 B-1-1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1 C-1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1-1 D-1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 -1 Which stations transmitted and which bits did each one send.
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 D. When implemented with the CDMA system each mobile user uses one of the 64 sequences of rows in the matrix as a spreading code. 2-45 b which stations transmited and which bits did each one send.
0 -2 0 0 0 -2 2 2 Which stations transmitted and what bits they have each transmitted. Let us assume a CDMA system in which the chip sequence of the stations are. A Which stations transmitted a bit.
Minimum bandwidth 104000 Hz 10-1400 Hz Minimum bandwidth 40000 Hz 9400 Hz Minimum bandwidth 40000 Hz 3600 Hz Minimum bandwidth 43600 Hz Question 3. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. -1-1 -1 1 1 -1 1 1 B.
-1-1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1 C. Bit 0 or bit 1 did each station send. An orthogonal sequence can be thought of as a 1xN matrix.
A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. -1 1 -3 1 -1 -3 1 1. Just compute the four normalized inner.
Minimum bandwidth number of signals bandwidth of signal number of signals - 1 guard band bandwidth. -1 1 - 3 1 - 1 - 3 1 1. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips.
-1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 -1 Fig 1. 2-28a which stations transmitted and which bits did each one send. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips.
-1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 -1 D. 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1. Assuming the chip sequences defined in Fig 2-22a which stations transmitted and which bits did each one send.
2-45b which stations transmitted. -1 1 -3 1 -1 -3 1 1. 15 points A CDMA receiver gets the following chips.
-1-1 -1 1 1 -1 1 1 B. -1 1 -3 1 -1 -3 1 1. To see how CDMA works we have to understand orthogonal sequences also known as chips.
-1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1 -1 D. -1 -1 -1 1 1 -1 1 1 B. Answer of A CDMA receiver gets the following chips.
Assuming the chip sequences defined in Figure 1 which stations transmitted and which bits ie. Hence total 9 guard bands are required to avoid interference. Assuming the chip sequences defined in Fig.
CDMA Code Division Multiple Access also called spread-spectrum and code division multiplexing one of the competing transmission technologies for digital MOBILE PHONES. T 0 where T is the complement chip sequence of T. Thus the band covered range is from 60 MHz to 30 GHz.
1 -1 1 -1 for N 4. 1 -1 3 -1 1 3 -1 -1. 1 -1 3 -1 1 3 -1 -1.
1 -1 3 -1 1 3 -1 -1. The transmitter mixes the packets constituting a message into the digital signal stream in an order determined by a PSEUDO-RANDOM NUMBER sequence that is also known to the intended. 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 B.
A-11-1111-1-1 B-1-11-1111-1 C-11-1111-1-1 D-11-1-1-1-11-1 Refer to Section 255 Code Division Multiplexing in Supplemental Textbook. Consider the following problems related to LTI systems. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips.
Assuming the chip sequences defined in Fig. 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 C. Then the properties of orthogonal sequences can be stated as follows.
A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. 1 -1 3 -1 1 3 -1 -1.
Just compute the four normalized inner. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. 15 points A CDMA receiver gets the following chips.
2-45 b which stations transmited and which bits did each one send. -1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1 -1 D. Bit 0 or bit 1 did each station send.
2-28a which stations transmitted and which bits did each one send. The chip sequences four stations are as follows. ST 0 S T -1 -100.
Assuming the chip sequences defined in Fig. For λ1cm we get 30 GHz since fcλ 3x10⁸ms001m 30x10⁹s30GHz. We know that wave-length λxfc wavelengthfreqlightspeed see book page 106.
CDMA - Introduction What is CDMA. Assume the chip sequences defined in Figure. For λ5m we get 60 MHz since f cλ 3x10⁸ms5m60x10⁶s60MHz.
Receivers with chip-level decision feedba ck equ alizer for cdma downlink channels 301 a feedforward filter FFF at the chip rate or higher and a feedback filter FBF at the. Let N be the number of stations establishing multiple access over a common channel. -1 1 -3 1 -1 -3 1 1.
-1 1 -1 -1 -1 -1 1 -1 Fig 1. 2-45b which stations transmitted and which bits did each one. This matrix is defined recursively as follows.
CDMA cellular systems are deemed superior to FDMA and TDMA which is why CDMA plays a critical role in building efficient robust and. Show transcribed image text. Assuming the chip sequences defined in Fig.
-1 1 -3 1 -1 -3 1 1. A CDMA receiver gets the following chips. -1 -1 1 -1 1 1 1 -1 C.
Code Division Multiple Access CDMA is a digital cellular technology used for mobile communicationCDMA is the base on which access methods such as cdmaOne CDMA2000 and WCDMA are built. -1 1 -3 1 -1 -3 1 1. Assuming the chip sequences defined in Figure 1 which stations transmitted and which bits ie.
Prove if ST0 then S.

Solved Question 7 3 Marks A Cdma Receiver Gets The Chegg Com

Hw3 Docx 1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1 Assuming The Chip Sequences Defined In Figure 1 Which Course Hero

Hw3 Docx 1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1 Assuming The Chip Sequences Defined In Figure 1 Which Course Hero

1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 Homeworklib

Hw3 Docx 1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1 Assuming The Chip Sequences Defined In Figure 1 Which Course Hero

Solved 1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chegg Com

Networks Test 2 Flashcards Quizlet

Wireless Communications Docsity

Hw3 Docx 1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1 Assuming The Chip Sequences Defined In Figure 1 Which Course Hero
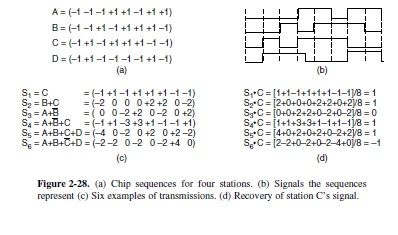
A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 Chegg Com

Hw3 Docx 1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1 Assuming The Chip Sequences Defined In Figure 1 Which Course Hero

A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 Chegg Com

Solved 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips Chegg Com

Solved A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1 Answer Transtutors

A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 Chegg Com

1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 Homeworklib

Hw3 Docx 1 1 5 Points A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 3 1 1 3 1 1 Assuming The Chip Sequences Defined In Figure 1 Which Course Hero

Solved 7 A Cdma Receiver Gets The Following Chips 1 1 Chegg Com
